17年1月的时候,使用siege工具对cgi进行压测,然而当时仅仅只是使用,没有好好了解内部的代码实现,最后压测出来的数据也是不如意,走了不少弯路 siege是多线程模型,n个并发通过创建n个线程来执行任务实现,同时还会有控制线程和计时线程,可以满足指定压测时间的要求。线程直接并发的控制主要通过互斥锁和等待条件变量来实现
首先大家来看下压测工具怎么使用
参数详解:
siege --help
SIEGE 3.0.6
Usage: siege [options]
siege [options] URL
siege -g URL
Options:
-
V, --version VERSION, prints the version number.
-
h, --help HELP, prints this section.
-
C, --config CONFIGURATION, show the current config.
#在屏幕上打印显示出当前的配置,配置是包括在他的配置文件$HOME/.siegerc中,
#可以编辑里面的参数,这样每次siege 都会按照它运行.
-
v, --verbose VERBOSE, prints notification to screen.
#运行时能看到详细的运行信息
-
q, --quiet QUIET turns verbose off and suppresses output.
-
g, --get GET, pull down HTTP headers and display the
transaction. Great for application debugging.
-
c, --concurrent=NUM CONCURRENT users, default is 10
#模拟有n个用户在同时访问,n不要设得太大,因为越大,siege 消耗本地机器的资源越多
-
i, --internet INTERNET user simulation, hits URLs randomly.
#随机访问urls.txt中的url列表项,以此模拟真实的访问情况(随机性)
-
b, --benchmark BENCHMARK: no delays between requests.
-
t, --time=NUMm TIMED testing where "m" is modifier S, M, or H
ex: --time=1H, one hour test.
#持续运行siege ‘n’秒(如10S),分钟(10M),小时(10H)
-
r, --reps=NUM REPS, number of times to run the test.
#重复运行测试n次,不能与 -t同时存在
-
f, --file=FILE FILE, select a specific URLS FILE.
#指定用urls文件,默认为siege安装目录下的etc/urls.txt
#urls.txt文件:是很多行待测试URL的列表以换行符断开,格式为:
#[protocol://]host.domain.com[:port][path/to/file]
-
R, --rc=FILE RC, specify an siegerc file
#指定用特定的siege配置文件来运行,默认的为$HOME/.siegerc
-
l, --log[=FILE] LOG to FILE. If FILE is not specified, the
default is used: PREFIX/var/siege.log
#运行结束,将统计数据保存到日志文件siege.log中,可在.siegerc中自定义日志文件
-
m, --mark="text" MARK, mark the log file with a string.
-
d, --delay=NUM Time DELAY, random delay before each requst
between 1 and NUM. (NOT COUNTED IN STATS)
#hit每个url之间的延迟,在0-n之间
-
H, --header="text" Add a header to request (can be many)
-
A, --user-agent="text" Sets User-Agent in request
-
T, --content-type="text" Sets Content-Type in request
例如压测命令如下:
/usr/local/bin/test/result.txt;/root/affiliu/siege -c 200 -r 750 -f /usr/local/bin/test/yace_buy_url_150000.txt -R /root/.siege/siege.conf -b 2>>/usr/local/bin/test/result.txt
-c代表并发量,实际上会低一点,-r是每个进程重复请求的次数,-f 指定请求的url文件 -b是请求和请求之间不要有延迟,2>>/usr/local/bin/test/result.txt 是吧统计结果重定向到这个文件下,-R /root/.siege/siege.conf这个是读取配置文件的路径 压测总共压测的请求数目为:200*750=150000
siege压测时候的一些注意点
修改siege的配置:
修改/root/.siege/siege.conf文件,修改里面的配置
limit配置,siege可以开的最大的进程数目,将它修改成1024
verbose配置,修改成false,减少每次请求之后io操作,从而减少请求与请求直接的延迟,提高压测的可靠性
修改压测机器的配置:
在/etc/security/limits.conf文件末尾添加
soft noproc 102400
hard noproc 102400
soft nofile 102400
hard nofile 102400
修改用户级的最大文件描述符限制,防止开进程开到一定数目之后报错
Siege输出结果
** SIEGE
2.72
** Preparing
300 concurrent users
for battle.
The server is now under siege.. done.
Transactions:
30000 hits
Availability:
100.00 %
Elapsed
time:
68.59 secs
Data transferred:
817.76 MB
Response
time:
0.04 secs
Transaction rate:
437.38 trans/
sec
Throughput:
11.92 MB/
sec
Concurrency:
17.53
Successful transactions:
30000
Failed transactions:
0
Longest transaction:
3.12
Shortest transaction:
0.00
然而在压测的过程中总是遇到一些问题,当设置的压测线程很大的时候,实际统计输出的执行线程数输出往往小很多,总感觉压不起来的样子(这里可能是由于之前siege代码里面有个bug(同事发现),导致tcp设置非阻塞不起作用,单纯的通过加大线程加大并发反而会线程切换过多导致效率降低),现在我们来看下代码,分析下
siege的实现
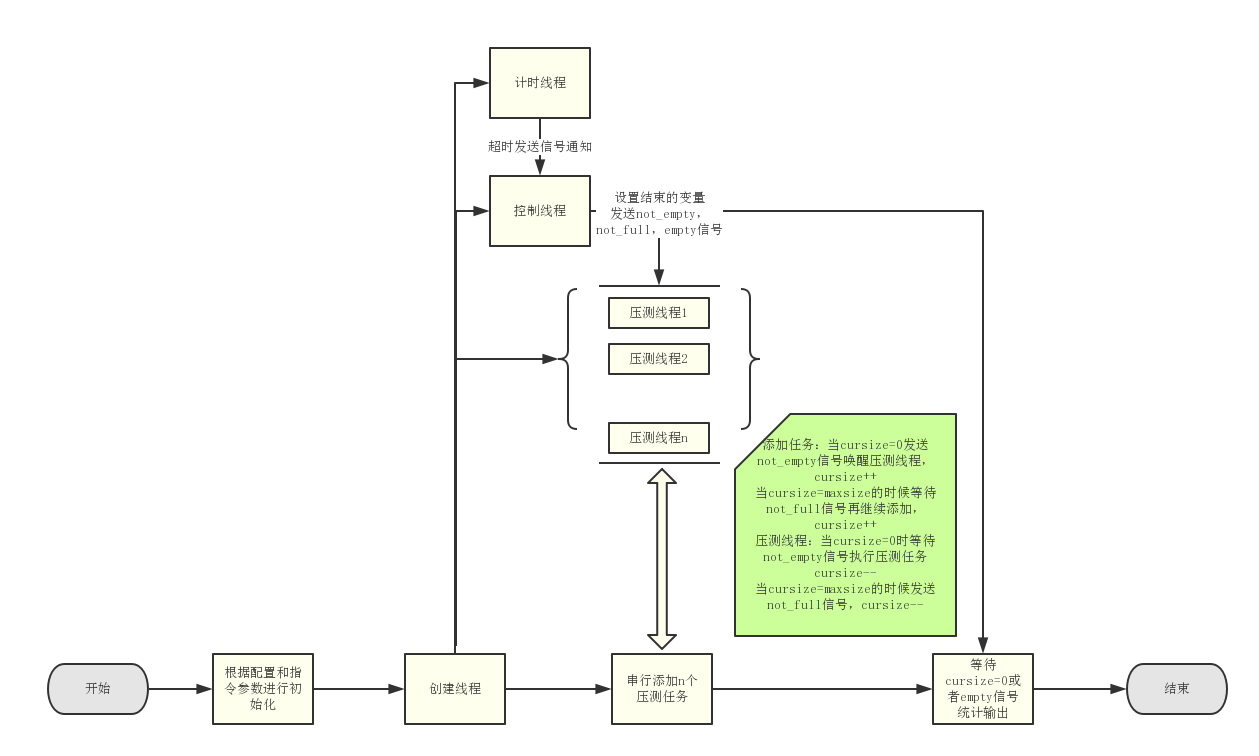
核心数据结构
CREW_T,在程序中所有线程共用的这样一个结构体实例,通过锁和信号量控制每个线程串行修改和获取压测任务
struct CREW_T
{
int size;
int maxsize;
int cursize;
int total;
WORK *head;
WORK *tail;
BOOLEAN block;
BOOLEAN closed;
BOOLEAN shutdown;
pthread_t *threads;
pthread_mutex_t
lock;
pthread_cond_t not_empty;
pthread_cond_t not_full;
pthread_cond_t empty;
};
CREW的存储的压测链表结构体WORD,压测时,线程从获取到结构体的函数指针和相应参数即可执行
typedef struct work
{
void (*routine)();
void *arg;
struct work *next;
} WORK;
每个线程分别维护的BROWSER_T结构体,存储压测url数组,存储该线程压测数据的统计结果
struct BROWSER_T
{
int id;
ARRAY urls;
......
};
核心代码简析
我们首先来看mian函数,整个框架也不太复杂,就是初始化,设置线程,等待回收线程,收集结果。其中线程的控制是我们比较需要注意的地方 main函数:
int
main(
int argc,
char *argv[])
{
......
__signal_setup();
__config_setup(argc, argv);
lines = __urls_setup();
if ((crew = new_crew(my
.cusers, my
.cusers,
FALSE)) ==
NULL) {
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"unable to allocate memory for %d simulated browser", my
.cusers);
}
if ((result = pthread_create(&cease,
NULL, (
void*)sig_handler, (
void*)crew)) <
0) {
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"failed to create handler: %d\n", result);
}
if (my
.secs >
0) {
if ((result = pthread_create(&timer,
NULL, (
void*)siege_timer, (
void*)cease)) <
0) {
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"failed to create handler: %d\n", result);
}
}
......
data = new_data();
data_set_start(data);
for (i =
0; i < my
.cusers && crew_get_shutdown(crew) !=
TRUE; i++) {
BROWSER B = (BROWSER)array_get(browsers, i);
result = crew_add(crew, (
void*)start, B);
if (result ==
FALSE) {
my
.verbose =
FALSE;
fprintf(stderr,
"Unable to spawn additional threads; you may need to\n");
fprintf(stderr,
"upgrade your libraries or tune your system in order\n");
fprintf(stderr,
"to exceed %d users.\n", my
.cusers);
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"system resources exhausted");
}
}
crew_join(crew,
TRUE, &status);
data_set_stop(data);
......
......
}
new_crew函数,n个压测线程的初始化,以及初始化信号和互斥锁,在这里压测线程就已经都建立成功了,然后都循环等到not_empty信号来触发执行。
CREW
new_crew(
int size,
int maxsize, BOOLEAN block)
{
int x;
int c;
CREW
this;
if ((
this = calloc(
sizeof(*
this),
1)) ==
NULL)
return NULL;
if ((
this->threads = (pthread_t *)malloc(
sizeof(pthread_t)*size)) ==
NULL)
return NULL;
this->size = size;
this->maxsize = maxsize;
this->cursize =
0;
this->total =
0;
this->block = block;
this->head =
NULL;
this->tail =
NULL;
this->closed =
FALSE;
this->shutdown =
FALSE;
if ((c = pthread_mutex_init(&(
this->lock),
NULL)) !=
0)
return NULL;
if ((c = pthread_cond_init(&(
this->not_empty),
NULL)) !=
0)
return NULL;
if ((c = pthread_cond_init(&(
this->not_full),
NULL)) !=
0)
return NULL;
if ((c = pthread_cond_init(&(
this->empty),
NULL)) !=
0)
return NULL;
for (x =
0; x != size; x++) {
if ((c = pthread_create(&(
this->threads[x]),
NULL, crew_thread, (
void *)
this)) !=
0) {
switch (errno) {
case EINVAL: { NOTIFY(ERROR,
"Error creating additional threads %s:%d", __FILE__, __LINE__);
break; }
case EPERM: { NOTIFY(ERROR,
"Inadequate permission to create pool %s:%d", __FILE__, __LINE__);
break; }
case EAGAIN: { NOTIFY(ERROR,
"Inadequate resources to create pool %s:%d", __FILE__, __LINE__);
break; }
case ENOMEM: { NOTIFY(ERROR,
"Exceeded thread limit for this system %s:%d", __FILE__, __LINE__);
break; }
default: { NOTIFY(ERROR,
"Unknown error building thread pool %s:%d", __FILE__, __LINE__);
break; }
}
return NULL;
}
}
return this;
}
crew_thread线程的执行函数,简单来说就是当cursize=0时等待not_empty信号执行压测任务cursize–,当cursize=maxsize的时候发送not_full信号,cursize–
private void
*
crew_thread(
void *crew)
{
int c;
WORK *workptr;
CREW
this = (CREW)crew;
while (TRUE) {
if ((c = pthread_mutex_lock(&(
this->
lock))) !=
0) {
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"mutex lock");
}
while ((
this->cursize ==
0) && (!
this->shutdown)) {
if ((c = pthread_cond_wait(&(
this->not_empty), &(
this->
lock))) !=
0)
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"pthread wait");
}
if (
this->shutdown == TRUE) {
if ((c = pthread_mutex_unlock(&(
this->
lock))) !=
0) {
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"mutex unlock");
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
workptr =
this->head;
this->cursize--;
if (
this->cursize ==
0) {
this->head =
this->tail = NULL;
}
else {
this->head = workptr->next;
}
if ((
this->block) && (
this->cursize == (
this->maxsize -
1))) {
if ((c = pthread_cond_broadcast(&(
this->not_full))) !=
0) {
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"pthread broadcast");
}
}
if (
this->cursize ==
0) {
if ((c = pthread_cond_signal(&(
this->empty))) !=
0){
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"pthread signal");
}
}
if ((c = pthread_mutex_unlock(&(
this->
lock))) !=
0) {
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"pthread unlock");
}
(*(workptr->routine))(workptr->arg);
xfree(workptr);
}
return(NULL);
}
crew_add函数,添加压测任务到crew的word链表里面,cursize=0时发送not_empty信号,每增加一个任务,cursize的值加一,当cursize=maxsize的时候等待not_full信号再继续添加,cursize值加一
BOOLEAN
crew_add(CREW crew,
void (
*routine)(),
void *arg)
{
int c;
WORK
*workptr;
if ((c
= pthread_mutex_lock(
&(crew
->lock)))
!= 0) {
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"pthread lock");
}
if ((crew
->cursize
== crew
->maxsize)
&& !crew
->block) {
if ((c
= pthread_mutex_unlock(
&(crew
->lock)))
!= 0) {
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"pthread unlock");
}
return FALSE;
}
while ((crew
->cursize
== crew
->maxsize )
&& (
!(crew
->shutdown
|| crew
->closed))) {
if ((c
= pthread_cond_wait(
&(crew
->not_full),
&(crew
->lock)))
!= 0) {
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"pthread wait");
}
}
if (crew
->shutdown
|| crew
->closed) {
if ((c
= pthread_mutex_unlock(
&(crew
->lock)))
!= 0) {
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"pthread unlock");
}
return FALSE;
}
if ((workptr
= (WORK
*)malloc(sizeof(WORK)))
== NULL) {
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"out of memory");
}
workptr
->routine
= routine;
workptr
->arg
= arg;
workptr
->next
= NULL;
if (crew
->cursize
== 0) {
crew
->tail
= crew
->head
= workptr;
if ((c
= pthread_cond_broadcast(
&(crew
->not_empty)))
!= 0) {
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"pthread signal");
}
}
else {
crew
->tail
->next
= workptr;
crew
->tail
= workptr;
}
crew
->cursize
++;
crew
->total
++;
if ((c
= pthread_mutex_unlock(
&(crew
->lock)))
!= 0) {
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"pthread unlock");
}
return TRUE;
}
start函数,真正的压测函数,选取需要执行的url并请求,具体的http,https和ftp的实现这次没有详细说明,有兴趣的可以看看实现,对自己代码编写会有不少帮助
void *
start(BROWSER
this)
{
......
/**
* 根据每个线程的需要执行数量,选择url进行调用和解析返回结果
*/
for (x =
0; x < len; x++, y++) {
URL tmp = array_get(
this->urls, y);
if (tmp != NULL && url_get_hostname(tmp) != NULL) {
this->auth.bids.www =
0;
if ((ret = __request(
this, tmp))==FALSE) {
__increment_failures();
}
}
if (my.delay >=
1) {
pthread_sleep_np(
(unsigned
int) (((
double)pthread_rand_np(&(
this->rseed)) /
((
double)RAND_MAX +
1) * my.delay ) +
.5)
);
}
else if (my.delay >=
.001) {
pthread_usleep_np(
(unsigned
int) (((
double)pthread_rand_np(&(
this->rseed)) /
((
double)RAND_MAX +
1) * my.delay *
1000000 ) +
.0005)
);
}
return NULL;
}
crew_join回收线程函数。结束的时候,当cursize不为0的时候,循环等待empty信号,empty信号只有在计时进程到时间 控制进程强制结束才发,等待empty信号并且设置了等待时间。在等待到了empty信号或者等待超时并且此时设置了结束或者已经没有压测任务了,退出。
BOOLEAN
crew_join(CREW crew, BOOLEAN finish,
void **payload)
{
if (finish
== TRUE) {
while ((crew
->cursize
!= 0)
&& (
!crew
->shutdown)) {
int rc;
struct timespec ts;
struct timeval tp;
rc
= gettimeofday(
&tp,
NULL);
if( rc
!= 0 )
perror(
"gettimeofday");
ts
.tv_sec
= tp
.tv_sec
+60;
ts
.tv_nsec
= tp
.tv_usec
*1000;
rc
= pthread_cond_timedwait(
&(crew
->empty),
&(crew
->lock),
&ts);
if (rc
==ETIMEDOUT) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(
&crew
->lock);
}
if (rc
!= 0) {
NOTIFY(FATAL,
"pthread wait");
}
}
}
return TRUE;
}
总结
总而言之,siege是一个非常方便的压测工具,支持http,https和ftp协议,提供了很全面的压测功能。 但是因为siege的线程控制主要是通过锁和信号来进行,线程执行压测任务时,需要先抢到锁,获取到压测任务。有n个压测线程相互竞争锁。siege的算并发数的算法为:所有线程的执行时间只和/压测总时间 ,每个线程开始工作时间不统一,压测的总时间的计算其实也不是很准确,这样子肯定算出来会比实际小。如果真的需要使用siege进行高并发,高精准的压测任务,还是需要好好读下代码并且进行适当的修改。
